Tag: Power Transmission
-
The Problems Associated with Embedded Power Generation
The rate of the development of energy sources that are alternatives to hydrocarbons is happening at a greater pace than any other time before; this is mainly because of the environmental reasons i.e. the limitation of carbon dioxide emissions and for the longer-term sustainability of energy supplies. The role played by such alternative energy sources…
-
Synchronous Compensators, What is their Purpose in Power Systems?
When designing a transmission or distribution system, the engineer must take into account not only the power requirement of the loads, but also the fact that they consume reactive power and to the same degree key, that networks include inductive and capacitive components which themselves absorb or generate reactive power. Power is generated and consumed…
-
What is the Function of Unified Power Flow Controller?
In a number of cases, it may be possible to increase the grid’s capacity through enhanced control of the active and reactive power flow in the transmission network independently of busbar voltage. The Unified Power Flow Controller (UPFC) provides the reactive shunt compensation, active and reactive series compensation and phase shifting. It is thus capable…
-
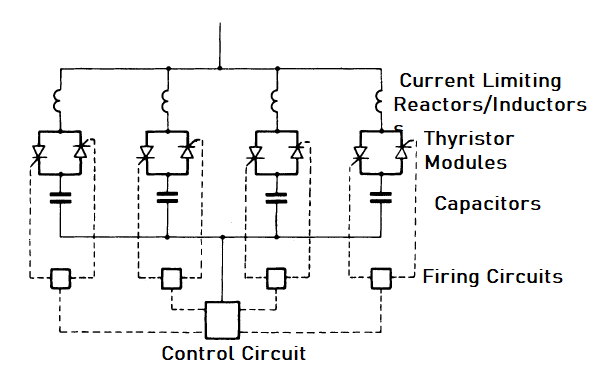
What are Flexible Alternating Current Transmission Systems (FACTS) Controllers?
Flexible AC Transmission Systems (FACTS) can be described as AC transmission systems incorporating power electronic-based controllers and other static controllers to boost controllability and increase power transfer capability. FACTS equipment that provides control of one or more of the parameters of an electrical network is often referred to as a FACTS controller. FACTS devices may…
-
The Principles of Power System Protection
The Function and Principles of Power System Protection The objective of power system protection is to detect faults or abnormal operating conditions and initiate corrective action. Principles of Power System Protection There are different principles used in accomplishing power system protection, we have discussed them in the following sections: Discrimination by Time In simple radial…
-
Overvoltage Protection Techniques & Equipment
Overvoltage Protection – Objective, Methods & Equipment The purpose of the protective equipment in a power system is to isolate the faulty section from the healthy system by initiating tripping for appropriate circuit breakers. This whole process must be carried out with minimum of delay and disturbance. Overvoltage, switching and other phenomena like lightning produce…
-
What is Corona Discharge in Power Transmission Conductors?
Corona and its Effects in Power Transmission Systems What is Corona? Corona is the term used to describe the violet glow or ‘brush’ discharge around conductors when the air is stressed beyond the ionization point without flashover developing. When an alternating potential difference is applied across two conductors whose spacing is large as compared to…
-
DC Transmission and Distribution
In most cases, the dc power is obtained from large ac power systems by employing converting mechanisms like synchronous or rotary converters, solid-state converters and motor-generator sets and so forth. The reasons why power generation is done in ac form rather than dc are: How DC Power is Obtained from AC Power A general layout…
-
Major Technologies for Smart Grid Implementation
Smart grid can enhance legacy electric systems (i.e. the traditional electricity infrastructure) by improving reliability and security; additional smart grid can offer economic benefits and cost savings, environmental improvement, and so forth. Generally smart grid represents the integration of digital technologies, sensors and other information and communication technologies to enable more efficient and reliable electricity…