Category: Electrical & Electronics Measurements
-
What is the function and application of a Modulation Analyzer?
Modulation analyzer is used in communication systems for investigating amplitude, frequency and phase-modulated RF signals. Also referred to as a precision receiver, it can measure carrier frequency and power in addition to modulating frequency, modulation depth, frequency deviation and so forth. It is applied in testing transmitters, RF signal generators, attenuators, and other communication circuits.…
-
Distortion Meter vs. Wave Analyzer, How do they Differ?
Though these two instruments may appear similar in their functionality, there are actually subtle differences between them in terms of their functions and operations. The distortion meter is used to measure the total harmonic distortion content in an input waveform whereas the wave analyzer is used to measure relative amplitude of single frequency components in…
-
Distortion Meter: Function, Components & Controls
The Function of a Distortion Meter A distortion meter is used to measure the total harmonic distortion content in an input waveform. The rms level of the distortion is usually measured as a percentage of the rms level of the complete waveform. Alternatively, a decibel measurement may be employed. A sine wave input to an…
-
How to Calibrate a DC Ammeter using a Potentiometer
We can calibrate a dc ammeter by connecting it in series with a precision resistor/standard resistor, and accurately measuring the resistor voltage drop. The level of ammeter current is determined by dividing the resistor voltage drop by its resistance value. When the resistor value is known precisely, and the voltage drop is measured by a…
-
Wave Analyzers: Function, Types & Applications
The Function of a Wave Analyzer Generally, a periodic waveform can be represented as a sum of a dc component and a series of sinusoidal harmonics. The analysis of a waveform entails the determination of the values of amplitude, frequency and at times the phase angle of the harmonic components. A wave analyzer is an…
-
Power Measurement in Fiber Optics, How it is Done
Optical Power The basic unit of measurement in fiber optics is the light power. Just like electric power, optic power is measured in watts. For light, the total energy Q is given by: Q = NQp Where Qp is the energy of a single photon and N is the number of photons, therefore: The Power…
-
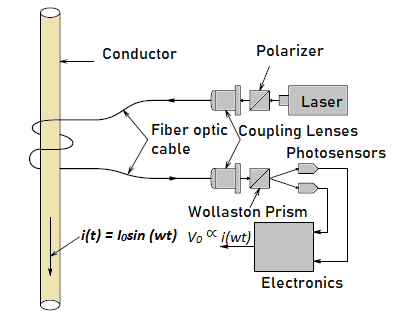
Magneto-Optic Current Sensors for High Voltage, High Power Transmission Lines
One of the key challenges in measuring the electrical current in high voltage, high power transmission lines, is that of measurement circuit isolation. One way of measuring heavy 60 Hz currents in a conductor is through the use of a current transformer. A current transformer typically consists of a number of turns of wire wound…
-
Digital Voltmeters: Basic Features, Operation & Applications
The digital voltmeter (DVM) displays measurement of ac or dc voltages as discrete numbers instead of a pointer deflection on a continuous scale as in analog instruments. A digital voltmeter basically consists of an analog-to-digital converter, a set of seven-segment numerical displays and the necessary BCD-to-seven-segment drivers. A digital voltmeter is a versatile and accurate…
-
Sweep Frequency Generator: Function, Features & Applications
Function & Features of a Sweep Frequency Generator A special type of signal generator which generates a sinusoidal output whose frequency is automatically varied or swept between two chosen frequencies is referred to as sweep frequency generator. One complete cycle of the frequency variation is termed as a sweep. The rate at which the frequency…
-
Digital Multimeter: Principle of Operation and How it is used
A Multimeter or volt-ohm-milliammeter (VOM) is an instrument used to measure current, voltage, and resistance. It can be used for measuring dc as well as ac voltages and currents. The two common types of multimeters include the analog multimeter and the digital multimeter. Analog multimeters employs a moving pointer mechanism that swings a long a…