Author: John Mulindi
-
Basic Features of Numerical Control
Numerical control is a form of digital control that is employed on machine tools such as milling machines and lathes to automatically cut and shape the work-piece without a human operator. Each machine has its own set of axes or parameters that must be controlled; case in point is a milling machine as illustrated in…
-
How to Size a Control Valve
Control valve sizing refers to the procedure determining the correct size of a valve body. A valve sizing equation for incompressible fluids is given by: Which is the same as: Where Cv is the valve flow coefficient/valve capacity P1 = Upstream fluid pressure P2 = Downstream fluid pressure ρ = Mass density of fluid Q…
-
Process Control System Design for a Distillation Unit
The aim of a typical control system is to force a given set of process variables to act in some desired and prescribed way by either fulfilling some requirements of the time or frequency domain or achieving the best performances as expressed by an optimization index. The scope of the control tasks varies widely. The…
-
Limit Switches vs. Proximity Sensors
An object can be used to activate a switch directly, producing an ON or OFF signal to indicate the presence of that particular object, alternatively we can use the presence of a nearby object to activate a sensor giving a signal which is either ON or OFF. A limit switch is a mechanical switch in…
-
Three-Position Control System: Operation & Typical Application
A three-position control is akin to two-point control, except that in this case, the controller has three states, such as forward-off-reverse, (or up-off-down, hot-off-cold, etc.). This is a control strategy that is usually applied in a system that has no specific self-seeking rest state. To help us demonstrate this control strategy, take a case of…
-
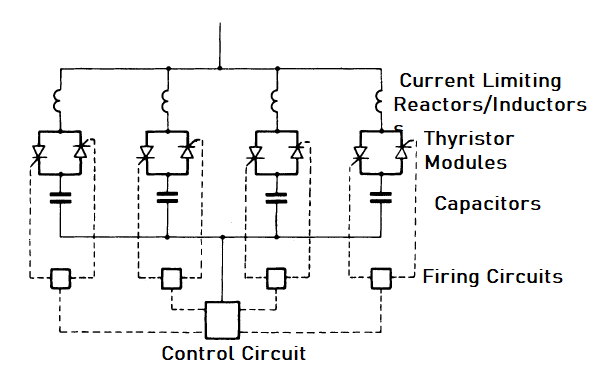
What are Flexible Alternating Current Transmission Systems (FACTS) Controllers?
Flexible AC Transmission Systems (FACTS) can be described as AC transmission systems incorporating power electronic-based controllers and other static controllers to boost controllability and increase power transfer capability. FACTS equipment that provides control of one or more of the parameters of an electrical network is often referred to as a FACTS controller. FACTS devices may…
-
The Connection of Green Energy Generation Plants to Power Systems: Key Factors to Consider
To prevent negative effects on the operation of the power system and equipment, a number of factors must be considered when connecting green energy generation plants to these systems. The following should be factored in: With the increased development of green energy generation plants, special aspects need to be considered such as the use of…
-
Causes of Power System Disturbances & Corrective Measures
Even though most protective system designs are built around individual components, system-wide disturbances in power systems are rather a frequent occurrence and a challenging issue for electric utility companies. When major disturbances occur in power systems, it is imperative to implement coordinated protection and control actions to stop the system degradation, restore the normal state…
-
Standard Process Signals for Industrial Instrumentation
Industrial measurement and control processes employ standard process signals that are used throughout all the industries. For instance, one of the most popular forms of signal transmission in modern industrial instrumentation systems is the 4-20 mA DC standard. The signal standards employed in industrial instrumentation are unique. Processes are referred to or measured as 0%…
-
Sources of Power Quality Problems
Power quality may be affected by a number of issues. Our discussion in this article focuses on various devices and events that lead to problems in power quality. The common sources of power quality problems include: Power Electronic Devices Power electronic devices cause power quality disturbances and they are also susceptible to them. Variable speed…